LCoS, which stands for Liquid Crystal On Silicon, is a display technology that shares similarities with LCD technology. It utilizes LCoS panels to control light, with CMOS chips serving as the circuit substrate and reflective layer. The liquid crystal is injected between the CMOS integrated circuit chip and a transparent glass substrate, allowing light to pass through the glass and liquid crystal material before being reflected from the chip’s surface after modulation.
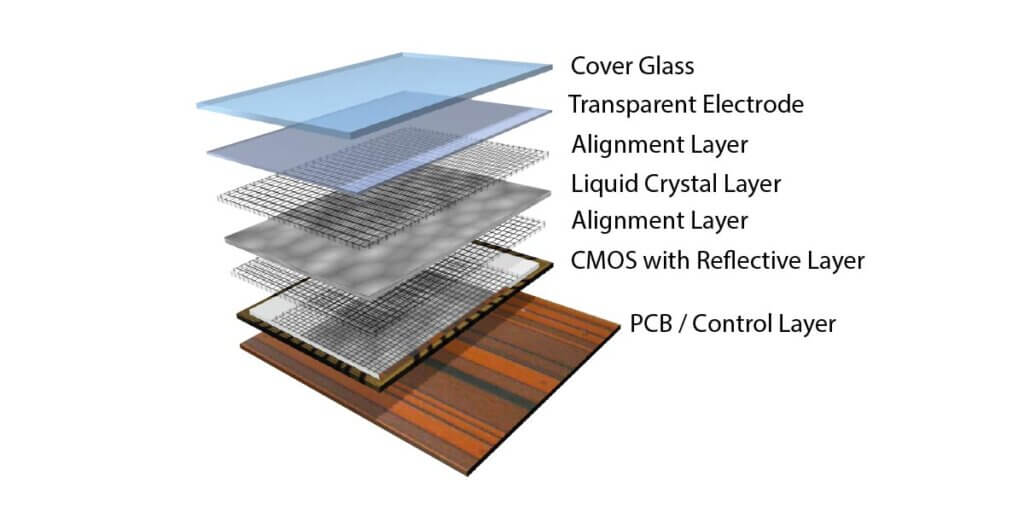
The fundamental principle of LCoS technology is akin to LCD technology, albeit with light projection controlled by LCoS panels. These panels consist of CMOS chips serving as both the circuit substrate and reflective layer, with the liquid crystal injected between the CMOS integrated circuit chip and a transparent glass substrate. The CMOS chip, when polished and smoothed, acts as a reflective mirror, allowing light to pass through the glass substrate and liquid crystal material before being reflected from the chip’s surface after modulation.

Advantages of LCoS technology:
- High-resolution panels: LCoS utilizes silicon wafer CMOS substrates, which, due to the material’s single-crystal silicon, boast excellent electron mobility, making it easier to achieve high-resolution panels.
- Improved light efficiency: As a reflective technology, LCoS can achieve light utilization rates of up to 40%, reducing power consumption while generating higher brightness.
- Cost-effectiveness: LCoS optical engines have relatively simple components, leading to lower production costs.
In summary, LCoS technology offers several advantages, including high-resolution panels, improved light efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. Its utilization of CMOS substrates and reflective technology contributes to enhanced performance and affordability, making it a compelling option for various display applications.
Relating Readings:
DLP vs LCoS vs 3LCD vs LCD Technologies
3LCD vs DLP vs LCOS: What Are the Differences?



