

With Huawei Hisilicon set to release a laser projector utilizing LCoS technology, it begs the question: how do these technologies differ from the mainstream DLP, 3LCD, and LCD technologies? Let’s delve into the distinctions between DLP, LCoS, 3LCD, and LCD technologies.


DLP, short for Digital Light Processing, relies on a Digital Micromirror Device (DMD) chip to manipulate mirrors to produce images. The DMD chip, situated within the optical engine, comprises thousands of tiny mirrors, each capable of tilting to reflect light. These mirrors can modulate light digitally, allowing for precise image projection.

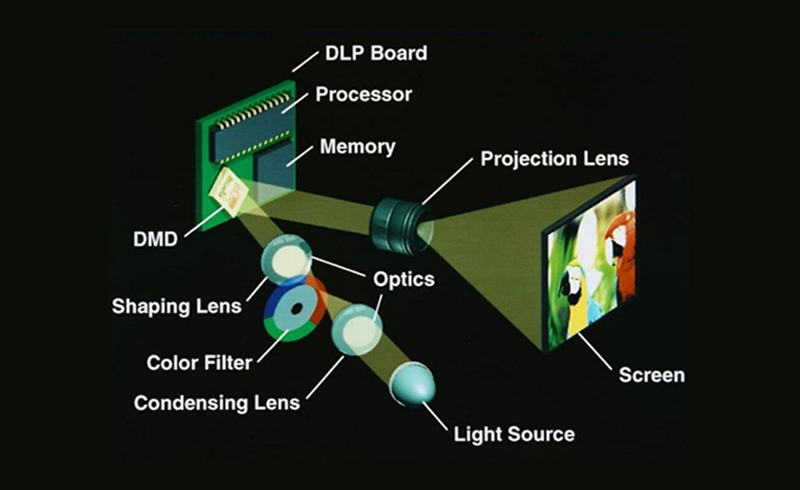
Advantages of DLP Technology:
LCoS, Liquid Crystal on Silicon, shares similarities with LCD technology but uses an LCoS panel to control light projection. The LCoS panel, situated between a CMOS chip and a transparent glass substrate, modulates light by altering the orientation of liquid crystals. Light passes through the glass substrate and the liquid crystal material, reflecting off the CMOS chip’s polished surface.
Advantages of LCoS Technology:
3LCD technology employs a prism to split white light from a source into red, green, and blue components, which then pass through independent liquid crystal panels. These panels modulate the intensity of light passing through each pixel, generating images that converge and project onto a screen.
Advantages of 3LCD Technology:
LCD, or Liquid Crystal Display, uses liquid crystals sandwiched between two glass panels to manipulate light. By applying electric currents to the liquid crystals, their orientation changes, allowing light to pass through and create images.
Advantages of LCD Technology:
Understanding the differences between these technologies can aid consumers in selecting the most suitable option for their needs, whether it’s for home entertainment, business presentations, or educational purposes.
Related Reading: